![]() +971 6 522 6368
+971 6 522 6368 ![]() +971-56-994-6523
+971-56-994-6523 ![]() info@resalahphysio.com
info@resalahphysio.com
Electrotherapy, also known as electrophysiotherapy or electrical stimulation therapy, is an advanced physiotherapy technique that utilizes controlled electrical currents to stimulate muscles and nerves. At Al Resalah Specialty Clinic in Sharjah, we use electrotherapy as a safe and effective solution to relieve pain, restore muscle function, and accelerate healing for a wide range of conditions.
✅ Conditions Treated with Electrotherapy:
Chronic and acute pain
Neck and back pain
Joint and muscle stiffness
Muscle weakness or atrophy
Post-surgical rehabilitation
Sports injuries
Nerve injuries
Swelling (edema) and inflammation
Arthritis and related disorders
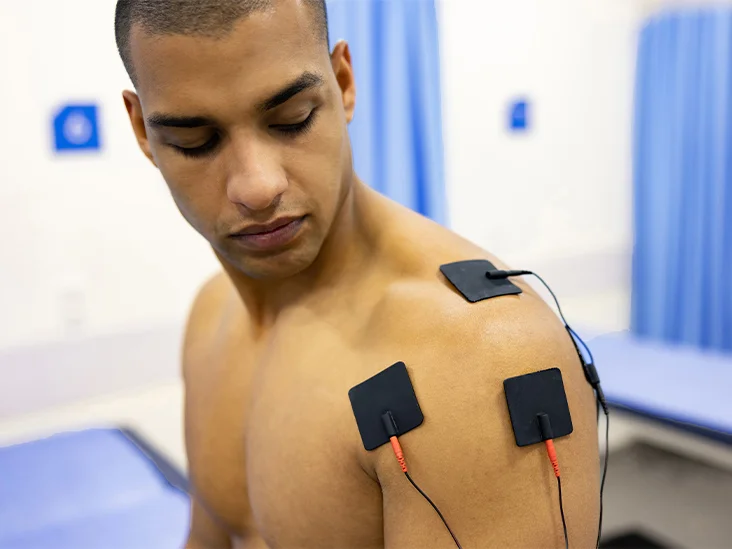
⚙️ Electrotherapy Modalities We Offer:
🔸 TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
Ideal for chronic pain, sciatica, arthritis, and post-injury pain.
Delivers low-voltage currents through the skin to block pain signals.
🔸 Interferential Current (IFC) Therapy
Effective for deep tissue pain, muscle spasms, and post-operative swelling.
Uses intersecting medium-frequency currents for deeper stimulation.
🔸 Galvanic Stimulation (GS)
Used for acute injuries, nerve damage, and swelling control.
Applies direct current (DC) to improve circulation and reduce edema.
🔸 Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
Beneficial in stroke recovery, post-fracture rehabilitation, and muscle re-education.
Promotes muscle contraction to restore strength and prevent atrophy.
🔸 Ultrasound Therapy
Although non-electrical, often combined with electrotherapy.
Helps treat ligament injuries, tendonitis, and soft tissue inflammation through deep tissue healing.
🔸 PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) Therapy
Used in bone healing, chronic pain conditions, and tissue regeneration.
Enhances cellular repair using electromagnetic pulses.
📍 Where Is Electrotherapy Done?
Electrotherapy treatments are performed in our Sharjah clinic’s physiotherapy department, in a dedicated, sanitized treatment area. Each session is administered by licensed physiotherapists using approved machines, customized to your diagnosis and therapy goals.
