![]() +971 6 522 6368
+971 6 522 6368 ![]() +971-56-994-6523
+971-56-994-6523 ![]() info@resalahphysio.com
info@resalahphysio.com
Laser Therapy
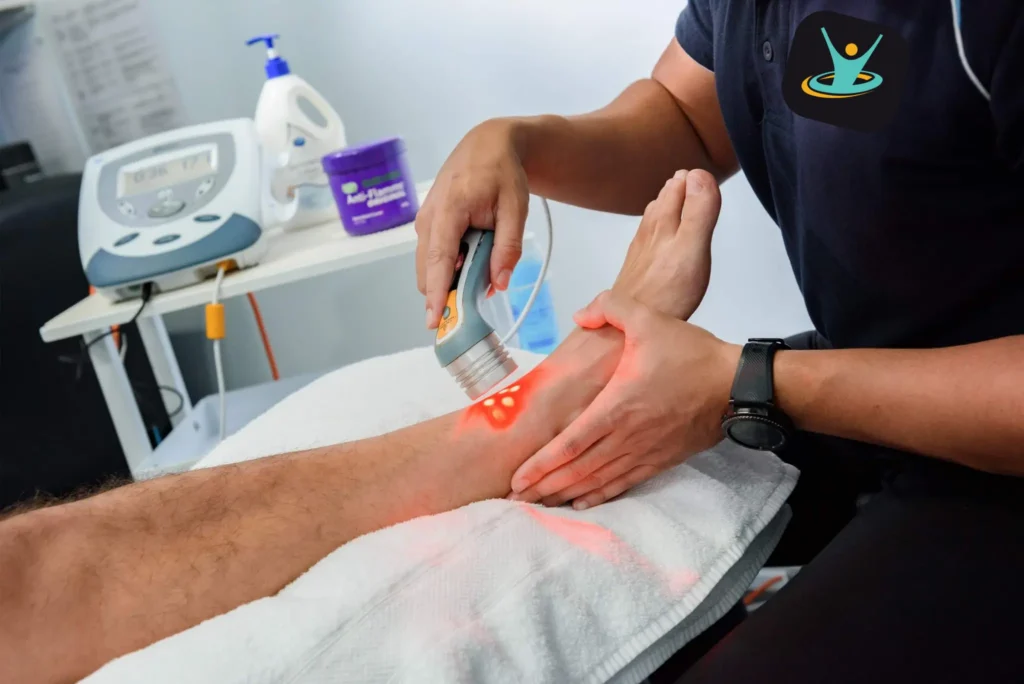
Laser physiotherapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or cold laser therapy, is a medical treatment that uses low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to stimulate cellular function and promote healing. Unlike surgical or ablative lasers, which are used for cutting or cauterizing tissue, the lasers used in physiotherapy are of lower intensity and do not produce heat.
Mechanism of Action:
- Cellular Effects: The light energy from lasers penetrates the skin and is absorbed by cells. This interaction triggers a series of cellular events that can enhance cell function and promote healing.
- Mitochondrial Stimulation: One proposed mechanism is the stimulation of cellular mitochondria, leading to increased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells.
Benefits:
- Pain Relief: Laser therapy is often used to alleviate pain associated with various conditions, such as musculoskeletal disorders, arthritis, and neuropathic pain.
- Inflammation Reduction: It may have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce swelling and promote tissue healing.
- Tissue Repair and Regeneration: Laser therapy is believed to stimulate tissue repair and regeneration, which can be beneficial for injuries and wounds.
Conditions Treated:
- Musculoskeletal Injuries: Laser therapy is commonly used for conditions like tendonitis, sprains, strains, and joint disorders.
- Chronic Pain: Conditions such as fibromyalgia and chronic lower back pain may be treated with laser therapy.
- Wound Healing: It can be used to promote the healing of wounds, including ulcers and surgical incisions.
Application:
- Contact and Non-contact Methods: Laser therapy can be applied directly to the skin (contact method) or using probes, wands, or other devices without direct skin contact (non-contact method).
- Dosage and Duration: The effectiveness of laser therapy may depend on factors such as the wavelength of light, energy density, treatment duration, and the specific condition being treated.
Safety Considerations:
- Low Risk: LLLT is generally considered safe when applied by trained professionals.
- Eye Protection: Eye protection is crucial for both the patient and the practitioner to avoid potential damage to the eyes from laser exposure.
Research and Controversies:
- Research: While there is some evidence supporting the effectiveness of laser therapy for certain conditions, more research is needed to establish its efficacy conclusively.
- Controversies: The use of laser therapy in physiotherapy is not without controversy, and opinions on its effectiveness can vary.
